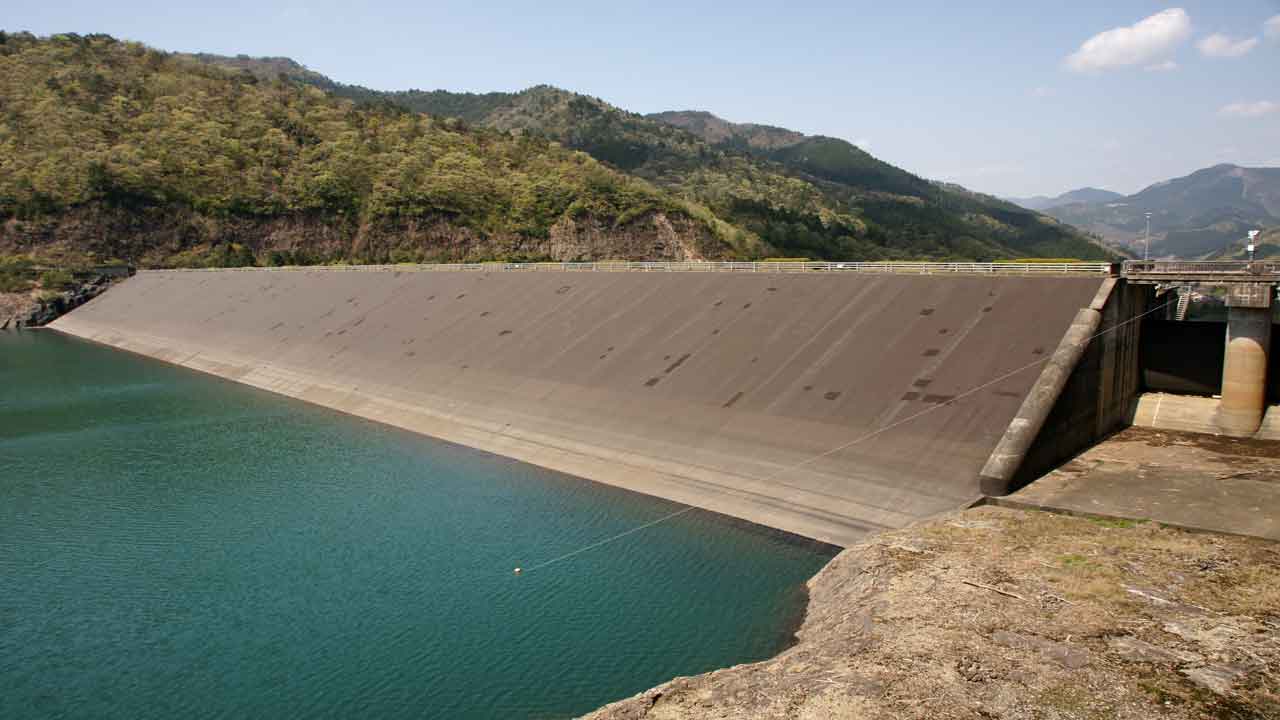
Earthen Dam.
Earthen dam utilizes natural materials with a minimum of processing and may be built with primitive equipment under conditions where any other construction material would be impracticable.
It is not surprising that the earliest known dams were of earth.
Modern developments in earth-moving equipment have resulted in decreased cost for earth moving as compared with an increase in the cost of concrete as a result of increased wage and material costs.
Earth dams are now competitive in cost with masonry in all sizes. The design of earth levees and dikes follows the same principles as for earth dams.
Unlike high-arch and gravity dams, which require a sound rock foundation, earth dam is readily adapted to earth foundations.
They are logical choices for many sites where foundation conditions make concrete dams unsatisfactory.
It should not be assumed that the construction of earth dam is a simple operation and that their design requires little more than rule-of-thumb criteria.
Numerous failures of poorly designed earth embankments make it apparent that earth dams require as much engineering skill in their conception and construction as any other type of dam.
In no other type of dam are the construction and design procedures so interdependent; continuous field observations of deformations and pore water pressures are often made during the construction period to evaluate the initial design.
Modifications of design based on these observations are not uncommon for large earth dams.
Read More: Types of Stones | Their Structure, Composition, and Properties.
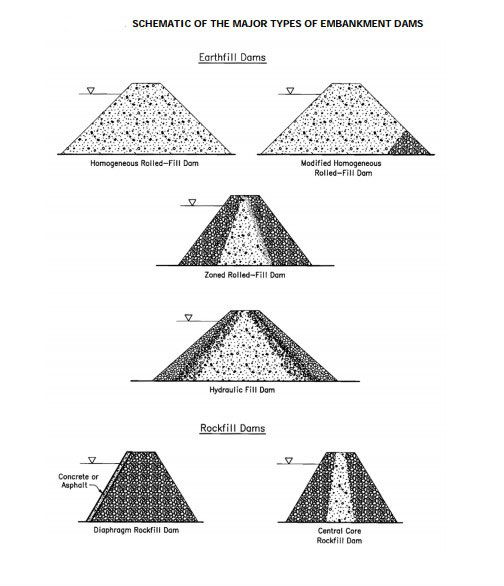
Types of Earth Dams.
The simple embankment is essentially homogeneous throughout, although a blanket of relatively impervious material may be placed on the upstream face.
Levees are often simple embankments, but large dams are rarely constructed in this manner.
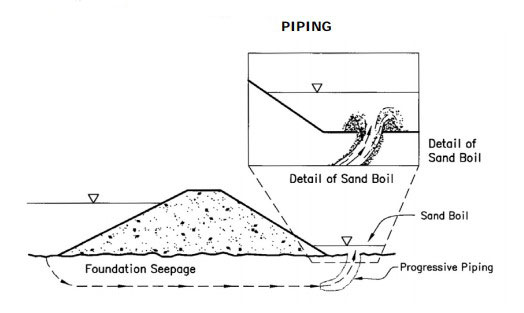
Zoned embankments usually have a central zone of selected soil material, to form a relatively impermeable core, a transition zone along both faces of the core to prevent piping through cracks which may form in the core,
….and outer zones of more perviousness material for stability.
This construction is widely used in earth dam and is selected whenever suitable materials are available.
Clay, even though highly impermeable, may not make the best core if it shrinks and swells too much.
The most satisfactory cores are of clay mixed with sand and tine gravel.
Diaphragm-type dams have a thin central section of concrete, steel, or timber which serves as a water barrier, while the surrounding earth or rock till provides stability.
Thin concrete sections are easily cracked by differential earth loads, and it is difficult to
form a perfectly watertight barrier of timber or steel.
In addition, the diaphragm must be tied into bedrock or a very impermeable material if excessive under-seepage is to be avoided.
Rock fill dams are built of coarse rock, which provides structural stability, with a concrete membrane on the upstream slope as a water barrier.
Methods of construction of Earth Dam.
Hydraulic-fill dams are constructed by using water for transporting the material to its final position in the dam.
The material is discharged from pipes along the outside edges of the fill, and the coarse materials are deposited soon after discharge,
…while the lines are carried into the central pool. The result is a zoned embankment with a relatively impermeable core.
This type of construction originated in the western United States as a result of experience with hydraulic mining.
Recent improvements in equipment for transporting and compacting dry fill have tended to discourage use of the hydraulic method.
Hydraulic fill is best suited for placing well-graded soils containing a considerable amount of coarse sand and gravel.
Adequate water supply is necessary, although some of the water may be recirculated.
Since the fill is saturated when placed, high pore pressures develop in the core material, and the embankment must be designed for stability under these pressures.
Because of the slow drainage of the water from the core, a considerable settlement is to be expected over a long period.
Read also: Water Cement Ratio – Definition, Calculation, Complete Guide.
The embankment is especially susceptible to earthquake damage until drainage is reasonably complete.
Semi-hydraulic-fill dams are constructed by dumping the fill material from trucks into its approximate position in the dam and sluicing the tines into a core.
Like the hydraulic-fill method, this procedure requires careful control to assure a satisfactory embankment.
Watch the Video Below for better understanding.
Dumping soil in a pool of water to produce a puddled core often washes the fines from the material and leaves a more permeable core than might have been obtained from proper dry compaction.
Numerous failures of hydraulic fill dams have occurred during construction.
Rolled-fill dams are constructed by placing selected materials in thin layers (6 to 18 inches), and compacting them with a heavy roller.
Some compaction may be obtained by proper routing of trucks and other construction equipment.
Usually, however, special equipment is used for compacting the fill. Both sheep-foot rollers and heavy pneumatic-tired rollers are used singly or in combination.
Ordinary road rollers have been used successfully on small projects.
In any case, the material should be placed at a moisture content near that for optimum density.
Coarse gravels are not suited for compaction by rolling, but vibrating equipment can be used.
Thanks for reading don’t forget to share this article.

It is really helpful.
please send for me your information about earth dam with calculation
Heyyy What’s the major material used for the construction of earthen dam is that soil or concrete